概述
本文是个人对Leetcode上链表题目的总结。
题目类型
链表拼接
链表拼接,对于头结点不会变化的情况下,可以直接拼接,比如题目[旋转链表]。而对于头结点可能变化,则通常需要设置一个哑结点dummy,将需要的结点拼接到这个哑结点之后,最后返回dummy.next即可。
代码
// 示例,两数相加
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = dummy;
int incr = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
if (l1 != null) {
incr += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
incr += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr.next = new ListNode(incr % 10);
curr = curr.next;
incr /= 10;
}
if (incr > 0) {
curr.next = new ListNode(incr);
}
return dummy.next;
}
题目
- 2. 两数相加:同时遍历两个链表,将相加结果拼接,注意最后进位
- 445. 两数相加 II:使用栈或者反转链表,再进行链表相加的操作
- 369. 给单链表加一:结果反转拼接
- 21. 合并两个有序链表:同时遍历两个链表,根据大小拼接
- 23. 合并K个升序链表:利用分治思想,问题变成合并两个有序链表
- 1669. 合并两个链表:分别得到两个链表拼接位置的前后结点,然后拼接
- 86. 分隔链表:按规则拆分为两个子链表,然后拼接
- 328. 奇偶链表:按规则拆分为两个子链表,然后拼接
- 203. 移除链表元素:移除结点需要其前结点,因此设置哑结点,利用prev指针来删除
- 面试题 02.01. 移除重复节点:利用哈希去重,删除结点需要有前结点指针
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素:元素只出现一次,因此跳过后续与当前结点相同的结点
- 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II:删除重复元素,指针指向未重复元素,判断后结点是否重复,来决定指针的移动
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点:使用哑结点,将第一个结点和第二个结点按顺序进行拼接
- 61. 旋转链表:计算出真正移动的k,对链表进行切分,然后拼接
- 138. 复制带随机指针的链表:先在原链表每个结点后拼接复制结点,然后对复制结点设置random指针,最后将复制结点分离出来
- 147. 对链表进行插入排序:若当前结点需要插入,则遍历头部,拼接到指定位置
链表反转
我们需要当前结点与前一个结点交换位置,因此,我们需要两个指针。
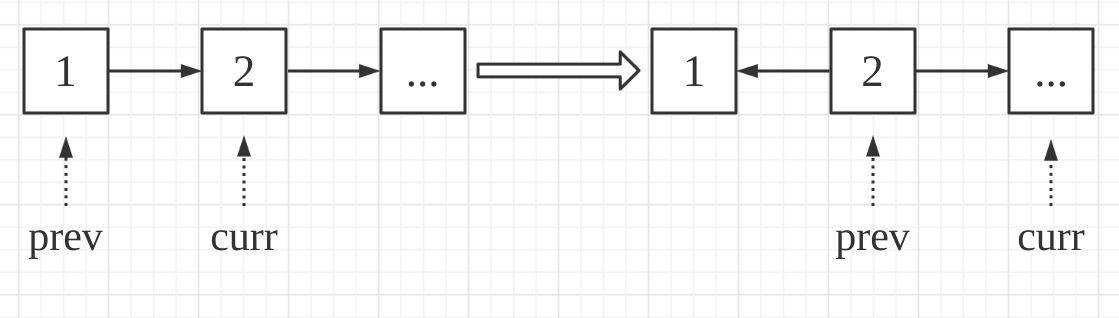
代码
// 单链表反转
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
// 双向链表反转
public Node reverse(Node head) {
Node prev = null;
while (head != null) {
Node next = head.next;
head.next = prev;
head.prev = next; // 相较于单向链表反转,增加前驱指针操作
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
题目
- 206. 反转链表:反转整个链表
- 92. 反转链表 II:对范围内的子链表反转,然后再拼接回原链表
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表:对一组进行反转,然后拼接回原链表,继续下一次循环
- 143. 重排链表:对右半部分进行反转,然后与左半部分链表进行拼接
- 234. 回文链表:对右半部分进行反转,然后与左半部分链表对比结点值,是否满足回文
获取倒数第K个结点
链表只能从头开始遍历,要获得倒数第K个结点,需要遍历n = size - k。使用双指针进行遍历,第一个指针先遍历
k个结点,那么之后该指针最多遍历n个结点。因此让第二个指针此时和它一起遍历到结束。
代码
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
head = head.next;
}
return head.val;
}
同理,如果想要获得链表中间结点,使用快慢指针即可:
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
题目
- 面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点:获得倒数第N+1个结点,删除后继结点
- 876. 链表的中间结点:快慢指针
链表是否有环
使用快慢指针,如果存在环,那么两个指针必定会相遇。
代码
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
题目
- 141. 环形链表:快慢指针
- 142. 环形链表 II:快慢指针判断是否有环,有环则头指针和慢指针一起遍历,相遇时就是环的头结点
链表相交
使用双指针同时遍历,如果一个链表遍历完,则继续再另外一个链表遍历。如果相交,则两个指针会遇到相同结点。
代码
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode currA = headA, currB = headB;
while (currA != null || currB != null) {
if (currA == null) {
currA = headB;
}
if (currB == null) {
currB = headA;
}
if (currA == currB) {
return currA;
}
currA = currA.next;
currB = currB.next;
}
return null;
}
题目
- 160. 相交链表:双指针